Biomedical Waste Rules 2011 Pdf
Municipal solid waste Wikipedia. Municipal solid waste MSW, commonly known as trash or garbage in the United States and as refuse or rubbish in Britain, is a waste type consisting of everyday items that are discarded by the public. Garbage can also refer specifically to food waste, as in a garbage disposal the two are sometimes collected separately. CompositioneditThe composition of municipal solid waste varies greatly from municipality to municipality,1 and it changes significantly with time. In municipalities which have a well developed waste recycling system, the waste stream mainly consists of intractable wastes such as plastic film and non recyclable packaging materials. At the start of the 2. UK consisted of coal ash from open fires. In developed areas without significant recycling activity it predominantly includes food wastes, market wastes, yard wastes, plastic containers and product packaging materials, and other miscellaneous solid wastes from residential, commercial, institutional, and industrial sources. Most definitions of municipal solid waste do not include industrial wastes, agricultural wastes, medical waste, radioactive waste or sewage sludge. Waste collection is performed by the municipality within a given area. The term residual waste relates to waste left from household sources containing materials that have not been separated out or sent for reprocessing. Waste can be classified in several ways but the following list represents a typical classification Biodegradable waste food and kitchen waste, green waste, paper most can be recycled although some difficult to compost plant material may be excluded6Recyclable materials paper, cardboard, glass, bottles, jars, tin cans, aluminum cans, aluminum foil, metals, certain plastics, fabrics, clothes, tires, batteries, etc. Inert waste construction and demolition waste, dirt, rocks, debris. Electrical and electronic waste WEEE electrical appliances, light bulbs, washing machines, TVs, computers, screens, mobile phones, alarm clocks, watches, etc. Composite wastes waste clothing, Tetra Packs, waste plastics such as toys. Hazardous waste including most paints, chemicals, tires, batteries, light bulbs, electrical appliances, fluorescent lamps, aerosol spray cans, and fertilizers. Toxic waste including pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides. Gang Game Downloads. Biomedical waste, expired pharmaceutical drugs, etc. Components of solid waste managementeditThe municipal solid waste industry has four components recycling, composting, disposal, and waste to energy via incineration. There is no single approach that can be applied to the management of all waste streams, therefore the Environmental Protection Agency, federal agency of the United States of America, developed a hierarchy ranking strategy for municipal solid waste. The Waste Management Hierarchy is made up of four levels ordered from most preferred to least preferred methods based on their environmental soundness Source reduction and reuse recycling or composting energy recovery treatment and disposal. CollectioneditThe functional element of collection includes not only the gathering of solid waste and recyclable materials, but also the transport of these materials, after collection, to the location where the collection vehicle is emptied. This location may be a materials processing facility, a transfer station or a landfill disposal site. Waste handling and separation, storage and processing at the sourceeditWaste handling and separation involves activities associated with waste management until the waste is placed in storage containers for collection. Handling also encompasses the movement of loaded containers to the point of collection. Separating different types of waste components is an important step in the handling and storage of solid waste at the source. Biomedical Waste Rules 2011 Pdf' title='Biomedical Waste Rules 2011 Pdf' />Segregation and processing and transformation of solid wasteseditThe types of means and facilities that are now used for the recovery of waste materials that have been separated at the source include curbside kerbside in the UK collection, drop off and buy back centers. The separation and processing of wastes that have been separated at the source and the separation of commingled wastes usually occur at a materials recovery facility, transfer stations, combustion facilities and disposal sites. Transfer and transporteditThis element involves two main steps. First, the waste is transferred from a smaller collection vehicle to larger transport equipment. The waste is then transported, usually over long distances, to a processing or disposal site. DisposaleditToday, the disposal of wastes by land filling or land spreading is the ultimate fate of all solid wastes, whether they are residential wastes collected and transported directly to a landfill site, residual materials from materials recovery facilities MRFs, residue from the combustion of solid waste, compost, or other substances from various solid waste processing facilities. A modern sanitary landfill is not a dump it is an engineered facility used for disposing of solid wastes on land without creating nuisances or hazards to public health or safety, such as the problems of insects and the contamination of ground water. ReusingeditIn the recent years environmental organizations, such as Freegle or Freecycle Network, have been gaining popularity for their online reuse networks. These networks provide a worldwide online registry of unwanted items that would otherwise be thrown away, for individuals and nonprofits to reuse or recycle. Therefore, this free Internet based service reduces landfill pollution and promotes the gift economy. Image/708/biomedical-waste-management-ppt-44.jpg]];var lpix_1=pix_1.length;var p1_0= [[558' alt='Biomedical Waste Rules 2011 Pdf' title='Biomedical Waste Rules 2011 Pdf' />LandfillseditLandfills are created by land dumping. Land dumping methods vary, most commonly it involves the mass dumping of waste into a designated area, usually a hole or sidehill. After the waste is dumped, it is then compacted by large machines. When the dumping cell is full, it is then sealed with a plastic sheet and covered in several feet of dirt. This is the primary method of dumping in the United States because of the low cost and abundance of unused land in North America. Landfills pose the threat of pollution, and can intoxicate ground water. B0052E200000578-3181663-Even_as_bio_medical_waste_is_increasing_every_year_inefficient_h-a-69_1438378970759.jpg' alt='Biomedical Waste Rules 2011 Pdf' title='Biomedical Waste Rules 2011 Pdf' />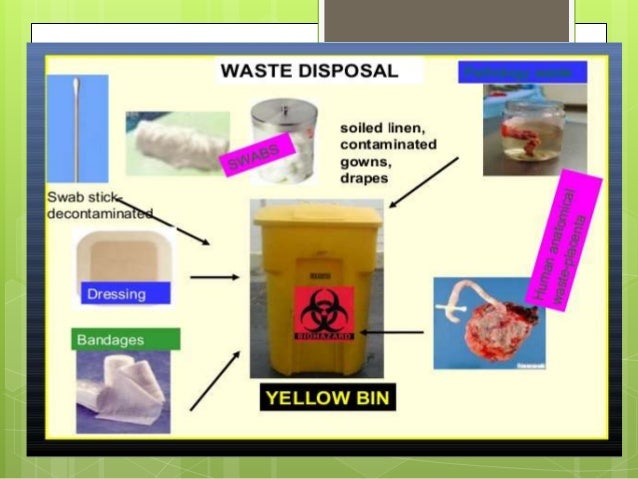 Acknowledgements This publication is dedicated to the memory of Matthew Gubb, who passed away during the development of the Global Waste Mangement Outlook GWMO. As one of the Souths most innovative institutions in teaching and learning, Kennesaw State University offers undergraduate, graduate and doctoral degrees across two. The signs of pollution are effectively masked by disposal companies and it is often hard to see any evidence. Usually landfills are surrounded by large walls or fences hiding the mounds of debris. Large amounts of chemical odor eliminating agent are sprayed in the air surrounding landfills to hide the evidence of the rotting waste inside the plant. Energy generationeditMunicipal solid waste can be used to generate energy. Several technologies have been developed that make the processing of MSW for energy generation cleaner and more economical than ever before, including landfill gas capture, combustion, pyrolysis, gasification, and plasma arc gasification. While older waste incineration plants emitted a lot of pollutants, recent regulatory changes and new technologies have significantly reduced this concern. United States Environmental Protection Agency EPA regulations in 1. Clean Air Act have succeeded in reducing emissions of dioxins from waste to energy facilities by more than 9. The EPA noted these improvements in 2. See alsoeditReferenceseditKumar, Sunil Dhar, Hiya Nair, Vijay V. Bhattacharyya, J. K. Vaidya, A. N. Akolkar, A.
Acknowledgements This publication is dedicated to the memory of Matthew Gubb, who passed away during the development of the Global Waste Mangement Outlook GWMO. As one of the Souths most innovative institutions in teaching and learning, Kennesaw State University offers undergraduate, graduate and doctoral degrees across two. The signs of pollution are effectively masked by disposal companies and it is often hard to see any evidence. Usually landfills are surrounded by large walls or fences hiding the mounds of debris. Large amounts of chemical odor eliminating agent are sprayed in the air surrounding landfills to hide the evidence of the rotting waste inside the plant. Energy generationeditMunicipal solid waste can be used to generate energy. Several technologies have been developed that make the processing of MSW for energy generation cleaner and more economical than ever before, including landfill gas capture, combustion, pyrolysis, gasification, and plasma arc gasification. While older waste incineration plants emitted a lot of pollutants, recent regulatory changes and new technologies have significantly reduced this concern. United States Environmental Protection Agency EPA regulations in 1. Clean Air Act have succeeded in reducing emissions of dioxins from waste to energy facilities by more than 9. The EPA noted these improvements in 2. See alsoeditReferenceseditKumar, Sunil Dhar, Hiya Nair, Vijay V. Bhattacharyya, J. K. Vaidya, A. N. Akolkar, A.